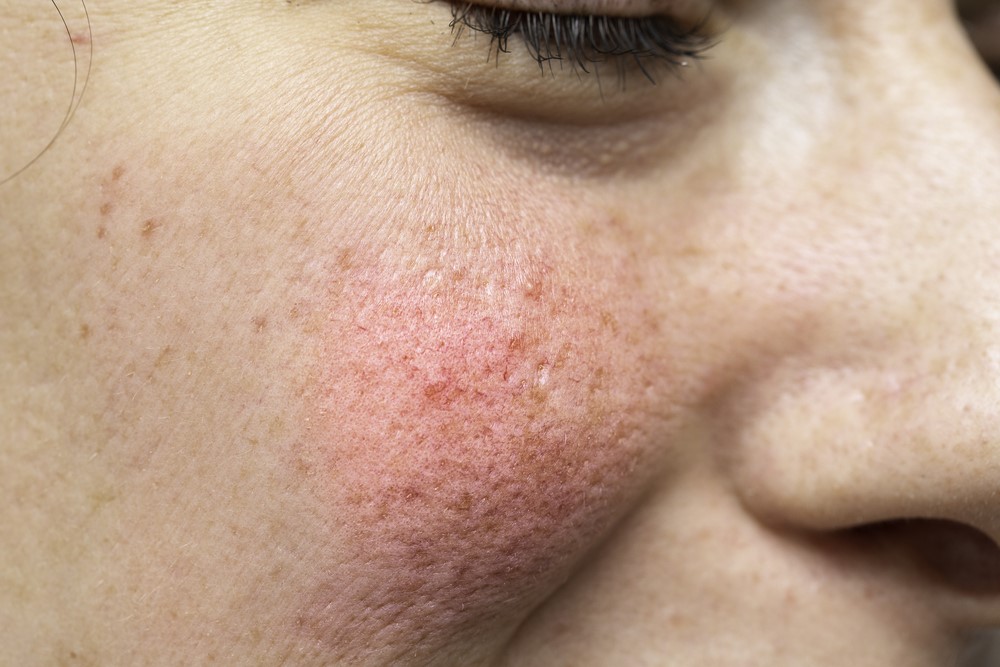
-
 OPI Nail Polish
1 ×
$94,
OPI Nail Polish
1 ×
$94,
-
 Sunscreen Lotion
1 ×
$89
Sunscreen Lotion
1 ×
$89
-
 Wholesale Liquid
1 ×
$75
Wholesale Liquid
1 ×
$75
-
 Hair Dryers
1 ×
$72
Hair Dryers
1 ×
$72
-
 Argan Hair oil
1 ×
$81
Argan Hair oil
1 ×
$81
Subtotal: $43
.png)